OrientationDicomStandard
1.Coordinate System
1a. Equipment Based
(obsolete)
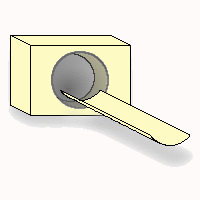
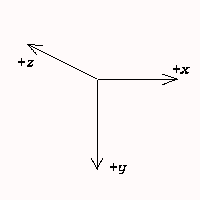
"When facing the front of the gantry (equipment device), and with the gantry in a neutral (untilted) position, the x-axis is increasing to the right; the y-axis is increasing down (gravitational attraction); and the z-axis is defined as the line orthogonal to x and y, with increasing values from the front to the back of the gantry." (From a Papyrus 2.3 document: UIN/HCUG 1990, 91)
 |  |
| Fig.: Front view of imaging device | Fig.: Equipment based coordinate system |
However obsolete for DICOM, this coordinate system was in use for Acr/Nema 2.0, the old predecessor of DICOM.
1b. Patient Based
"The direction of the axes is defined fully by the patient's orientation. The x-axis is increasing to the left hand side of the patient. The y-axis is increasing to the posterior side of the patient. The z-axis is increasing toward the head of the patient. The patient based coordinate system is a right handed system, i.e. the vector cross product of a unit vector along the positive x-axis and a unit vector along the positive y-axis is equal to a unit vector along the positive z-axis ..."
"... If a patient lies parallel to the ground, face-up on the table, with his feet-to-head direction the same as front-to-back direction of the imaging equipment, the direction of the axes of the patient based coordinate system and equipment based coordinate system in previous versions of the DICOM Standard will coincide" (From the NEMA Standards Publication PS3.3(199X)
Well, now we have an idea of how our coordinate system is orientated beyond any doubt! Ofcourse it still depends on how our patient was lying on the bed. A brief summary gives:
X-axis: Right (hand) -> Left (hand)
Y-axis: Anterior (front) -> Posterior (back)
Z-axis: Inferior (feet) -> Superior (head)
2. Image Origin
The origin of an image (slice) - be it tranversal, sagittal or coronal - is always considered in the upper left corner from where the image is filled; pixel by pixel, from left to right (columns); from top to bottom (rows) ... just like regular image arrays are structured. The 3D coordinate values of this origin are based on the coordinate system described above (patient or equipment based).
3. Unit Vectors
Next to the origin, the DICOM standard also uses two unit vectors placed on the image origin. One unit vector along the row of the image and one unit vector along the image column. Two type of directions are related to these vectors:
- the direction of both vectors according to the patient (patient based coordinate system)
- the direction cosines of both vectors along all three axes in the coordinate system
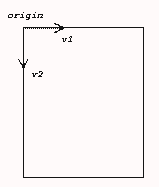
Fig.: Image with origin and two unit vectors
<< Patient/Slice Orientation | Documentation | (X)MedCon Supported >>
